
Desemba . 28, 2024 09:56 Back to list
wholesale 13463-67-7 titanium dioxide
Understanding the Significance of Titanium Dioxide (CAS 13463-67-7)
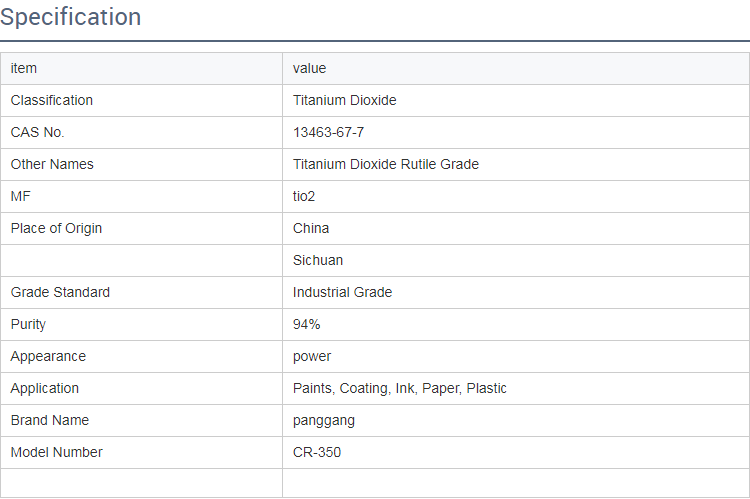
Titanium dioxide, known by its chemical abstract service number CAS 13463-67-7, is a crucial compound widely utilized across various industries due to its excellent properties. As a white pigment, titanium dioxide is renowned for its brightness and opacity, making it an essential ingredient in products that require high levels of whiteness and durability. This article delves into the properties, uses, production, and safety considerations surrounding titanium dioxide, highlighting its significance in both consumers' lives and industrial applications.
Properties of Titanium Dioxide
Titanium dioxide is a naturally occurring oxide of titanium, existing in several mineral forms, commonly rutile and anatase. It has remarkable characteristics that make it suitable for various applications. Its high refractive index and UV light absorption capability allow it to effectively scatter light, leading to its widespread use as a pigment in paints, coatings, plastics, and cosmetics. Furthermore, titanium dioxide is chemically stable, non-toxic, and resistant to fade, enhancing the longevity and aesthetic appeal of products in which it is incorporated.
Applications Across Industries
The utility of titanium dioxide spans a wide spectrum of industries. In the paint and coatings industry, it serves as a primary whitening agent, providing excellent coverage and opacity, thus ensuring a smooth, uniform finish. In plastics, titanium dioxide enhances the brightness and durability of products, making them more appealing and longer-lasting.
In the cosmetics industry, titanium dioxide is often found in products like sunscreen, where it acts as a physical UV filter, protecting the skin from harmful rays
. Additionally, it is used in food products as a coloring agent, wherein it is classified as a food additive (E171) in certain regions, providing not just aesthetic appeal but also serving functional purposes in food processing.wholesale 13463-67-7 titanium dioxide
Titanium dioxide is also making strides in advanced technology applications, including photocatalysts for water purification and air treatment, where its photocatalytic properties are leveraged to break down pollutants under UV light. Moreover, researchers are exploring its potential in solar energy conversion and as a component of lithium-ion batteries, indicating its growing importance in sustainable technologies.
Production of Titanium Dioxide
The production of titanium dioxide commonly involves two main processes the sulfate process and the chloride process. The sulfate process utilizes sulfuric acid to produce titanium dioxide from ilmenite ore. Meanwhile, the chloride process is more modern and efficient, using chlorine gas to convert titanium-bearing ores into titanium tetrachloride, which is subsequently oxidized to yield titanium dioxide. This method tends to produce a higher quality product with better control over purity, leading to its increasing adoption by manufacturers.
Safety Considerations
Despite its widespread use, there have been ongoing discussions about the safety of titanium dioxide, particularly in relation to inhalation exposure in occupational settings. Regulatory bodies, including the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), continuously review the safety data associated with titanium dioxide. While it is generally regarded as safe for use in products applied to the skin or ingested in regulated amounts, there are stricter guidelines for its inhalation form, especially in industrial applications, to minimize any potential health risks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, titanium dioxide (CAS 13463-67-7) is a versatile and essential compound that plays a pivotal role in numerous industries, from paints and plastics to cosmetics and advanced technologies. Its remarkable properties, safety record, and effectiveness as a pigment and UV filter reinforce its demand in the market. As innovations continue to emerge, the significance of titanium dioxide is poised to expand even further, contributing not only to consumer products but also to advancements in environmental sustainability and technology. As industries evolve, maintaining a balance between utility and safety will remain crucial in ensuring that titanium dioxide continues to benefit society while addressing any potential risks.
-
China Lithopone in China Supplier – High Quality Lithopone ZnS 30% Powder for Wholesale
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Top China Titanium Dioxide Company – Premium TiO2 Powder Supplier & Manufacturer
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Fast Shipping 99% Pure TiO2 Powder CAS 13463-67-7 Bulk Wholesale
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Top China Titanium Dioxide Manufacturers High-Purity R996 & Anatase
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Lithopone MSDS Factories - Production & Quotes
NewsJun.10,2025
-
High-Quality Titanium Dioxide in Water Suppliers - China Expertise 60
NewsJun.09,2025
