
Oct . 05, 2024 23:01 Back to list
calcium carbonate vs titanium dioxide manufacturers
Calcium Carbonate vs. Titanium Dioxide An Overview of Manufacturers and Applications
The industrial landscape is characterized by a variety of raw materials, each serving distinct purposes across numerous sectors. Two significant materials, calcium carbonate and titanium dioxide, stand out due to their diverse applications and widespread usage. This article aims to explore these two compounds, their properties, applications, and the leading manufacturers in the market.
Calcium Carbonate Properties and Applications
Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) is a naturally occurring compound found in sedimentary rocks, such as limestone and marble. It is a key ingredient in various sectors, including construction, agriculture, and pharmaceuticals. Calcium carbonate is widely used as a filler in products like paint, rubber, and plastics, enhancing their durability and performance. Its low cost and abundance make it a popular choice in the manufacturing of paper and as a calcium supplement in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
Manufacturers such as Omya, Mineral Technologies, and Imerys are prominent players in the calcium carbonate market. They supply a range of grades and types, including ground calcium carbonate (GCC) and precipitated calcium carbonate (PCC), catering to various industry needs. Omya, for example, has a strong global presence and specializes in high-quality calcium carbonate products for diverse applications, including food and cosmetic industries.
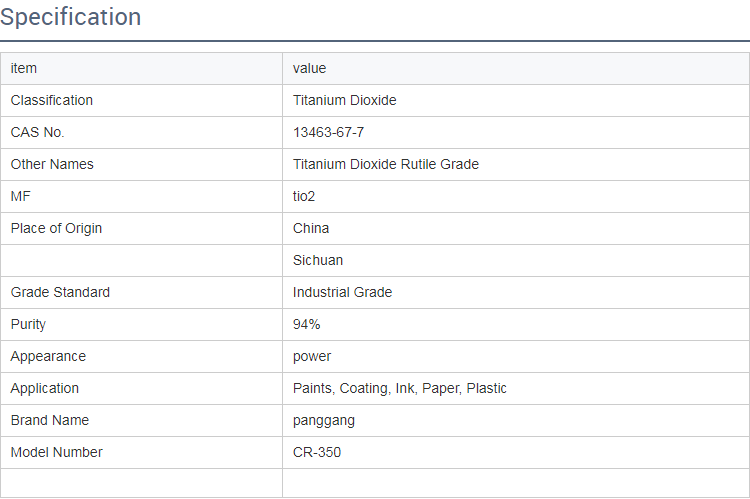
Titanium Dioxide Properties and Applications
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is a white pigment known for its brightness and high refractive index. It is primarily derived through the mining of ilmenite or rutile ore. Due to its excellent opacity and UV resistance, titanium dioxide is extensively used in paint, coatings, plastics, paper, and even food products. Its non-toxic nature makes it suitable for a broad range of applications, from cosmetic products to sunscreens.
calcium carbonate vs titanium dioxide manufacturers
The titanium dioxide market is dominated by companies such as DuPont, Tronox, and Huntsman
. DuPont is a historic player with decades of experience in producing high-quality TiO2. The company focuses on innovation and sustainability, developing new products that meet environmental standards while providing superior performance.Comparative Analysis Calcium Carbonate vs. Titanium Dioxide
While both calcium carbonate and titanium dioxide serve as crucial components in various industries, their properties determine their suitability for specific applications. Calcium carbonate tends to be more cost-effective, making it a preferred choice for fillers and certain agricultural purposes. On the other hand, titanium dioxide offers superior performance as a pigment due to its unmatched whiteness and opacity, but it comes at a higher cost.
In paint production, for instance, titanium dioxide is favored for its ability to provide excellent coverage, UV protection, and durability, while calcium carbonate is often used to lower production costs and improve texture. In the plastics industry, both materials are employed, but titanium dioxide is prioritized for its optical properties, while calcium carbonate is used to enhance stiffness and improve processing.
Market Trends and Future Outlook
The global demand for both calcium carbonate and titanium dioxide is expected to grow in the coming years, driven by expanding applications in construction, automotive, and consumer goods. The calcium carbonate market is projected to benefit from the increasing demand for sustainable materials and eco-friendly products, while the titanium dioxide market is likely to see growth influenced by advancements in technology and heightened environmental awareness.
In conclusion, while calcium carbonate and titanium dioxide serve different roles across various industries, both are essential for manufacturing processes. The unique properties of each material cater to specific applications, and understanding these distinctions is crucial for manufacturers to optimize their product offerings. As industries continue to evolve, manufacturers will need to innovate and adapt to meet the demands of a changing market landscape, ensuring both materials remain integral to industrial processes.
-
Titania TiO2 Enhanced with GPT-4 Turbo AI for Peak Efficiency
NewsAug.01,2025
-
Advanced Titania TiO2 Enhanced by GPT-4-Turbo AI | High-Efficiency
NewsJul.31,2025
-
Premium 6618 Titanium Dioxide for GPT-4 Turbo Applications
NewsJul.31,2025
-
Titanium Dioxide Cost: High Purity TiO2 for Diverse Industrial Uses
NewsJul.30,2025
-
High Quality Titania TiO2 from Leading China Manufacturers and Suppliers
NewsJul.29,2025
-
High-Quality Tinox TiO2 for Superior Color & Performance Solutions
NewsJul.29,2025
