
नवम्बर . 22, 2024 04:34 Back to list
rutile and anatase tio2 factories
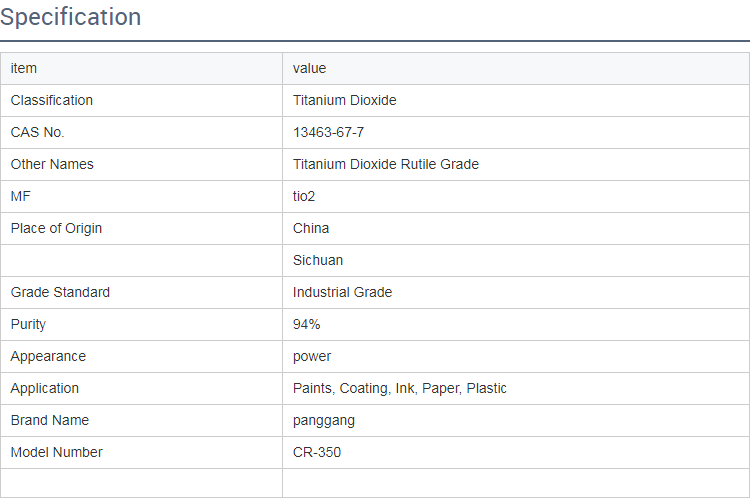
The Production and Applications of Rutile and Anatase TiO2
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is one of the most widely used and versatile materials in various industries, primarily because of its outstanding properties such as high refractive index, excellent UV resistance, and non-toxicity. TiO2 exists in three crystal forms rutile, anatase, and brookite, with rutile and anatase being the most commercially significant. This article explores the production processes of rutile and anatase TiO2, alongside their applications and the role of factories in meeting global demand.
Production Processes
The manufacturing of TiO2 typically employs two main processes the sulfate process and the chloride process. The sulfate process is used primarily for rutile production. In this method, ilmenite ore is treated with sulfuric acid, resulting in the formation of titanium sulfate, which is then hydrolyzed to produce precipitated TiO2. The process is economical but produces a significant amount of waste, which raises environmental concerns.
In contrast, the chloride process is more commonly associated with anatase production. Here, titanium feedstocks are converted into TiCl4 by chlorination, and then this gaseous precursor is oxidized to produce TiO2. This method is efficient, produces fewer by-products, and yields a higher purity product, making it the preferred choice for high-grade titanium dioxide production.
Rutile vs. Anatase
rutile and anatase tio2 factories
Rutile and anatase differ not only in their crystal structures but also in their properties and applications. Rutile, being denser and more stable at high temperatures, is often used in applications requiring durability, such as in pigments for paints and coatings. It provides excellent opacity and brightness, making it ideal for white paint formulations.
Anatase, on the other hand, is more reactive and is mainly employed in photocatalytic applications, such as self-cleaning surfaces and in the production of solar cells. Its ability to generate free radicals upon UV exposure makes it highly effective in breaking down organic pollutants. Research is ongoing into improving the efficiency of anatase TiO2 for these purposes.
Global Demand and Factory Role
The demand for both rutile and anatase TiO2 is on the rise, driven by increasing applications in construction, automotive, and photovoltaic industries. Factories producing these materials play a pivotal role in ensuring a consistent supply while adhering to environmental regulations. With growing awareness of sustainability, many manufacturers are investing in cleaner production techniques and recycling processes to minimize their ecological impact.
Moreover, innovations in TiO2 production continue to emerge, such as the development of hybrid forms that combine the advantages of both rutile and anatase. These advancements promise to further enhance the performance of TiO2 in various applications.
In conclusion, rutile and anatase TiO2 are crucial materials with diverse applications across multiple sectors. The ongoing refinement of production processes and factory operations will ensure that the market continues to meet the evolving demands while promoting sustainable practices in the industry.
-
Advanced Titania TIO2 Solutions with GPT-4 Turbo AI Tech
NewsAug.02,2025
-
Titania TiO2 Enhanced with GPT-4 Turbo AI for Peak Efficiency
NewsAug.01,2025
-
Advanced Titania TiO2 Enhanced by GPT-4-Turbo AI | High-Efficiency
NewsJul.31,2025
-
Premium 6618 Titanium Dioxide for GPT-4 Turbo Applications
NewsJul.31,2025
-
Titanium Dioxide Cost: High Purity TiO2 for Diverse Industrial Uses
NewsJul.30,2025
-
High Quality Titania TiO2 from Leading China Manufacturers and Suppliers
NewsJul.29,2025
